Hf Shape And Polarity

A polar molecule with two or more polar bonds must have a geometry which is asymmetric in.
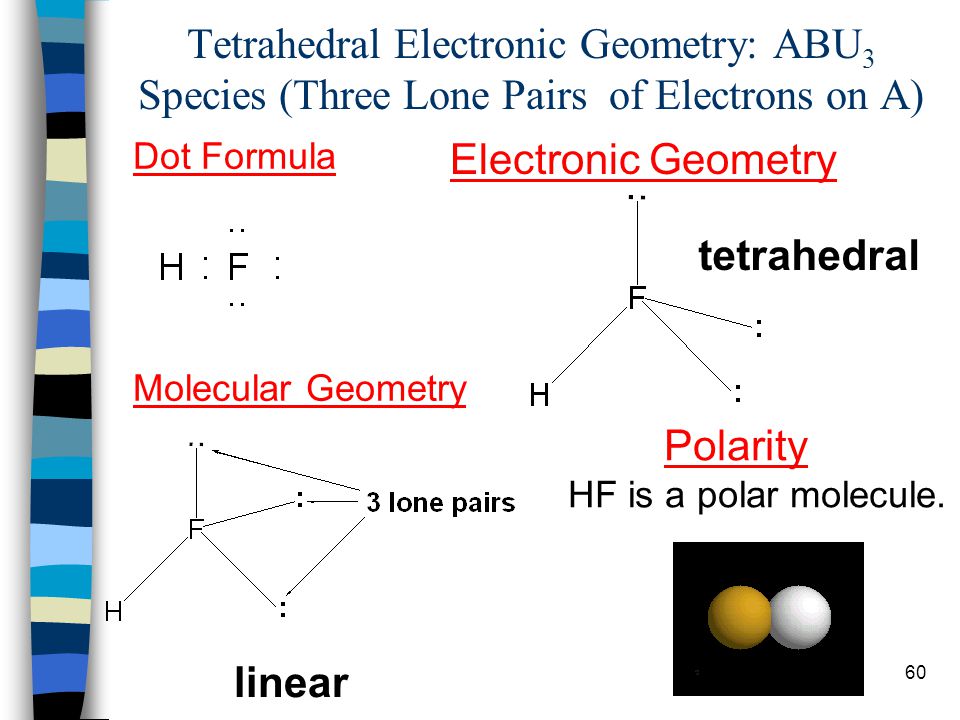
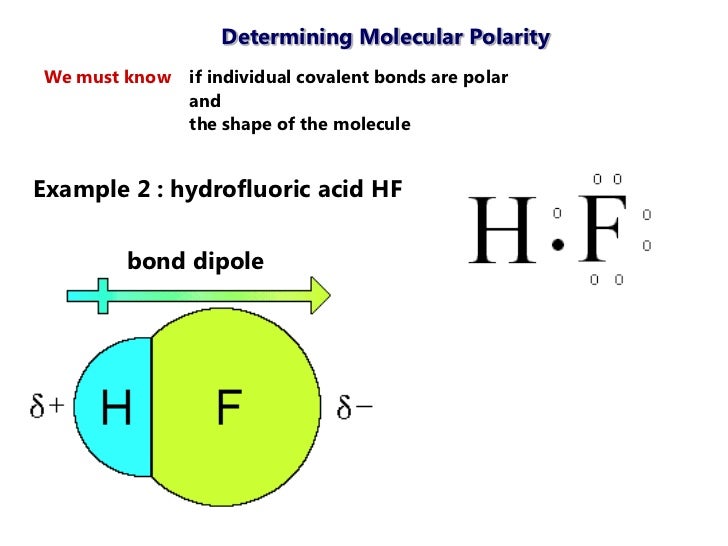
Hf shape and polarity. We start with the lewis structure and then use vsepr to determine the shape of the. A diatomic molecule like hf mentioned above has no issue of. Two identical atoms are found directly across the central atom from one another the molecule can be nonpolar. Cf 2 h 2 e.
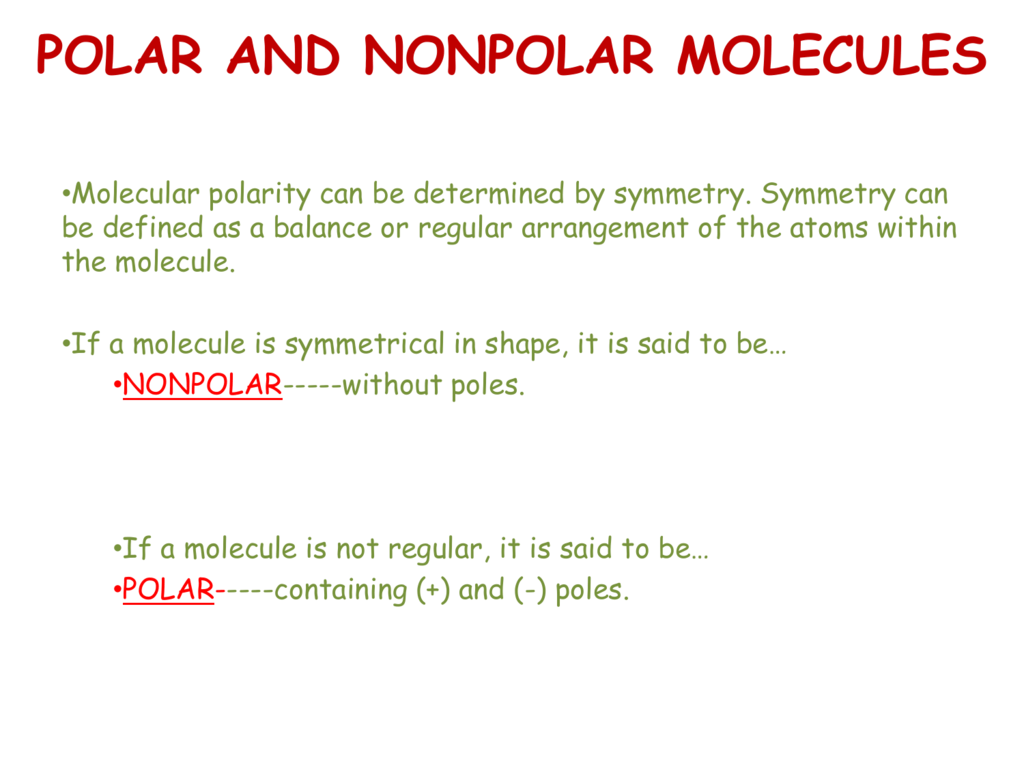
Polar molecules must contain polar bonds due to a difference in electronegativity between the bonded atoms. Sample learning goals predict bond polarity using electronegativity values. If the molecule has more than two atoms both shape and bond polarity determines the molecular polarity. N 2 o i.
Ni 3 trigonal pyramidal polar. The highly negative f in the hf molecule gets a slight negative charge while the h atom becomes slightly positive. Ccl 2 f 2 d. What is the shape and polarity of i2.
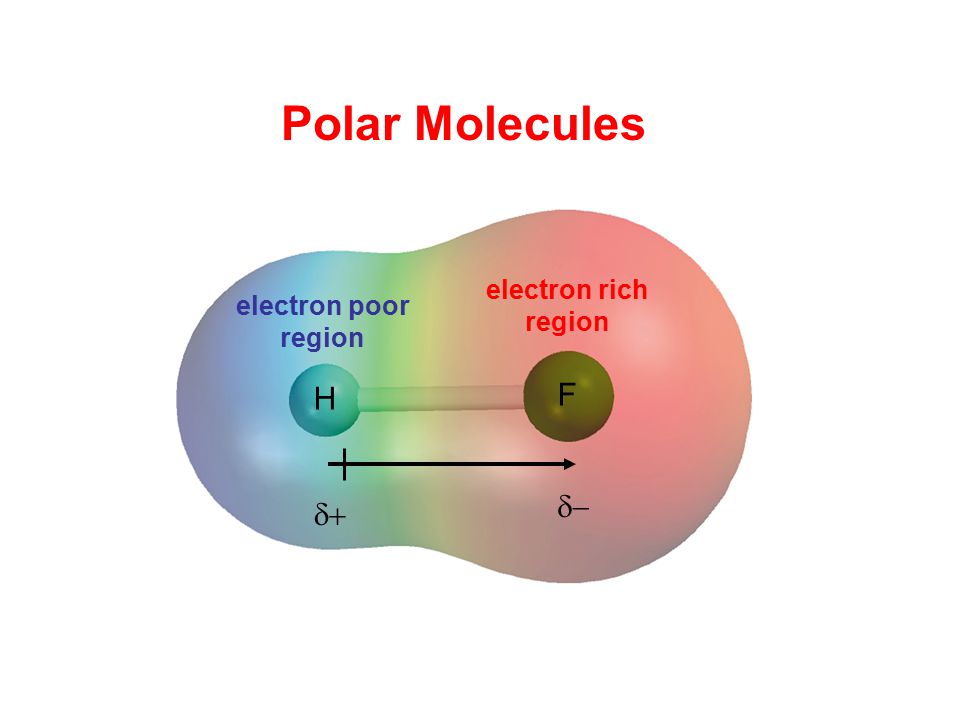
O 3 bent non polar t. Learn to determine if hf is polar or nonpolar based on the lewis structure and the molecular geometry shape. Water is polar because its bent shape means that the two polar bonds do not cancel. This results in a net dipole moment in a molecule.
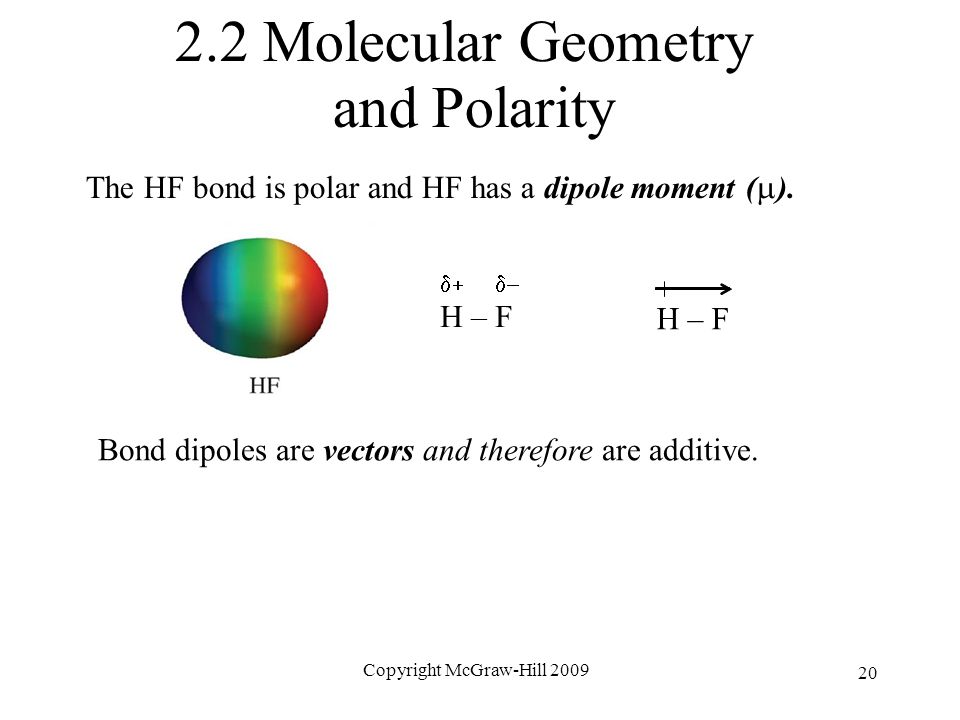
Ch 2 o f. Draw lewis structures name shapes and indicate polar or non polar for the following molecules. In ce co 2 the two polar bonds cancel each other out and the result is a nonpolar molecule. Hydrogen fluoride hf is a compound that is primarily polar.
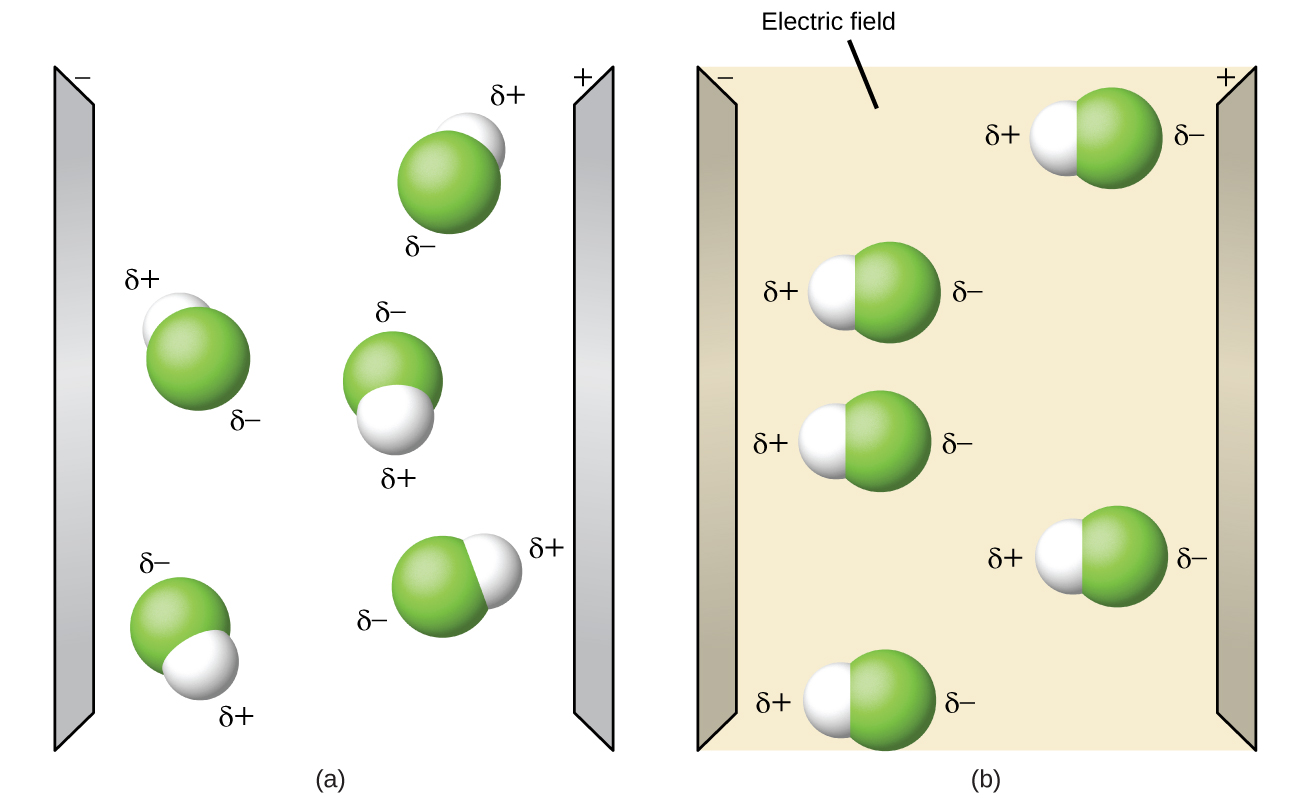
Polarity of hf is nonpolar and it s molecular shape is linear. Hf linear polar s. What is the shape and polarity of chcl3. See how the molecule behaves in an electric field.
Some other molecules are shown below see figure below. As long as the polar bonds are compensated for example. What is the shape and polarity of co2. What is the shape and polarity of ch4.
In chemistry polarity is a separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an electric dipole moment with a negatively charged end and a positively charged end. Molecular structure considers only the bonding pair geometry. H 2 o m. Change the bond angle to see how shape affects polarity.
This leads to the development of a partial negative charge on the f atom and a partial positive charge on the h atom leading to the generation of a dipole and hence polarity. What is the shape and polarity of nh3. What is the shape and polarity of h2s. Indicate polarity with a polar arrow or partial charges.
Change the electronegativity of atoms in a molecule to see how it affects polarity. This is due to the high electronegativity of the fluorine that pulls the shared electron pair between h and f more towards its side. The molecular geometry of a molecule affects its polarity.


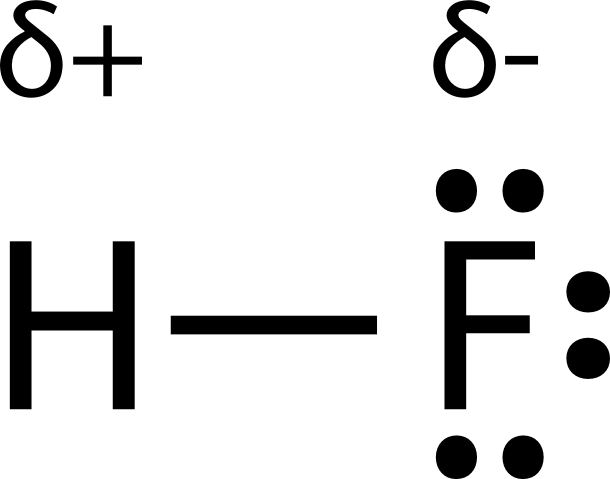




.PNG)